Working This is an instrument used for evaluating the tank atmosphere, prior to man entry, specifically for the presence of toxic gas. Hollow, glass tubes are inserted into a hand-held bellows pump through which a metered volume of the sample to be tested is drawn.The tubes are coated internally with a reagent and sealed at both ends. Different tubes are required for each type of toxic gas. The tubes are graduated externally. Just before use, the sealed ends are broken and the tube is fitted to the pump.As the sample is drawn through the tube by a recommended number of strokes of the … [Read more...]
Recommended Practices for Storage and Transport of Edible Oils and Fats
Introduction The international trade in oils and fats increases every year in volume and diversity. It included some 18 million tonnes of shipped cargo in 1984. The system involved in bringing the products from the harvest field to the end user is complex and inevitably a number of independent management is involved in processing, storage, and transport. It is clearly in the interest of all the parties involved that any deterioration in the products should be minimised. To this end, a number of trade associations have published advice for the benefit of their members. Individual sources … [Read more...]
Molasses – Carriage on Tankers
GENERAL Molasses is the thick dark brown syrupy liquid left after sucrose has been removed from the mother liquid in sugar manufacture. There is two type of molasses – cane molasses and beet molasses. Blackstrap molasses is the syrup from which no more sugar can be obtained economically.Synonym of molasses – Treacle.Main composition of molasses at 75 % Dry MatterCane molasses Beet molassesSucrose 30 – 40 % 48 – 52 %Reducing sugars 15 – 20 % 0.2 – 1.2 %Organic non-sugar matter 9 – 12 % 12 – 17 %Sulphated ash 3 – 11 % 3 – 10 % … [Read more...]
Vegetable, Palm and Soybean/Sunflower Oils – Carriage on Tankers
VEGETABLE OILS Prior loading of any Veg Oil cargoes, it should be noted that the last three cargoes must be lead-free.Also, ensure all Cargo Tanks, pipelines and pumps must be well drained and dried.The Veg Oils are very susceptible to Salt Water. Any contact with Sea water will result in rotting /damage of cargo.It should be ensured that after loading is completed; all cargo tanks are checked by Ship’s Officer along with attending surveyor, with a bottom sampler to ensure no water is trapped/loaded at Load Port.All Butterworth openings should have Oil resistant packing’s. … [Read more...]
What is VEF (Vessel Experience Factor) ?
The VEF is a factor to account for residual inherent measurement imprecision associated with ships's calibration and residual random measurement variations (both ship and shore). The VEF is a computation of the history of the Total Calculated Volume (TCV) loaded by the vessel adjusted for OBQ or ROB, compared with the TCV of shore measurements, typically a Bill of Lading in order to compute a load port VEF for the vessel.The VEF should always be used by the vessel to assess if the Bill of Lading quantity is reliable. It may also provide an indication of potential shortages on outturn at … [Read more...]
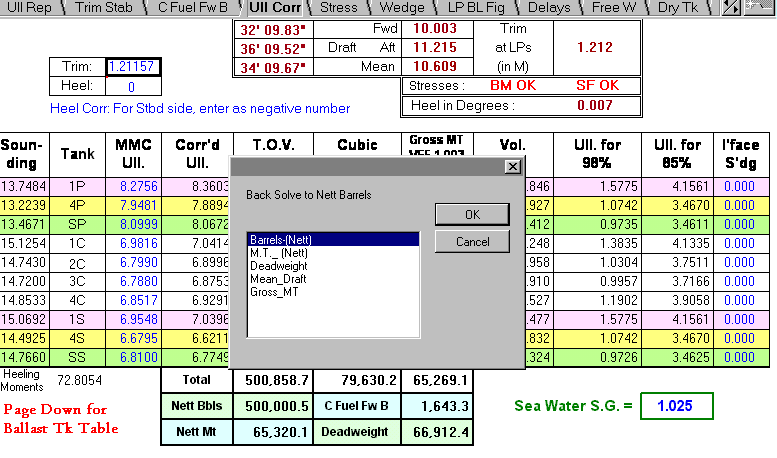
Cargo Calculations – Tanker Work
General An oil volume can only be measured at its prevailing temperature and it, therefore, follows that the standard volume must usually be calculated. Unfortunately, different countries have different standard (reference) temperatures.Generally, the reference temperatures are:In Eastern Bloc, Brazil 20oC; In Western Europe 15oC; In the USA 60oF. The situation is further confused in that there are primarily two volumetric units, which are:In metric countries the cubic meter (m ) In non-metric countries the barrel (Bbl).Combining a statement of volume … [Read more...]
Deck Water Seal – Inert Gas System on Tankers
Deck Water Seal In an inert gas system onboard Tanker ships, Deck water seal is the principal barrier. A water seal is fitted which permits inert gas to be delivered to the deck main but prevents any backflow of cargo gas even when the inert gas plant is shut down. It is vital that a supply of water is maintained to the seal at all times, particularly when the inert gas plant is shut down. In addition, drains should be led directly overboard and should not pass through the machinery spaces.There are different designs but one of three principal types may be adopted: Wet type This is … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) – Conventional Tanker Basics
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations.Prior arriving at the discharge port an exchange of information between the ship and the terminal will take place. Once the vessel is tied up at the terminal, a ship-shore checklist will have to be filled out. The general safety checks and precautions will be the same as given for the loadport. Since pumps will be running at the discharge port, special attention will have to be given to monitor the safe running of the pumps. Pumproom ventilation should be running throughout operations. Proper … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Loading) – Conventional Tanker Basics
Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations. Before a tanker approaches port, there are several factors that must be considered:Testing of cargo/ballast valves, sea valves, pipelines, pumps, inert gas systems, emergency stops. Preparedness of fire-fighting, life-saving and anti-pollution equipment. A pollution drill held before a ship arrives in port will serve the purpose of checking ail equipment. Any response during an emergency will be good since a drill had been executed recently. Preparation of tanks, including readiness of slop tanks. Planning for proper … [Read more...]
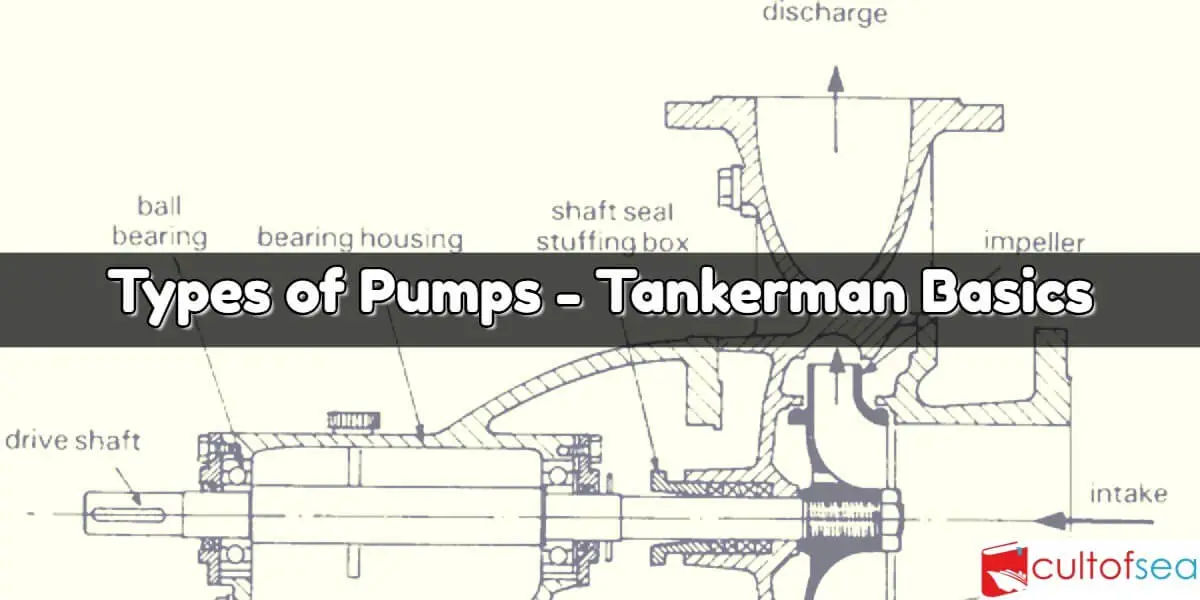
Pump Types / Characteristics – Tanker Basics
There are many types of pumps, each with its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Basically, pumps can be broadly categorised into 3 types :Non-positive-displacement pumps e.g. centrifugal pumps Positive displacement pumps e.g. reciprocating pumps, gear pumps, screw pumps, etc. Special devices like eductors which can also be included in this category.Centrifugal Pumps This type of pump does not have a self-priming capability. Consequently, it operates best only when there is a positive head on the suction side. However, this pump has the distinct capability of … [Read more...]