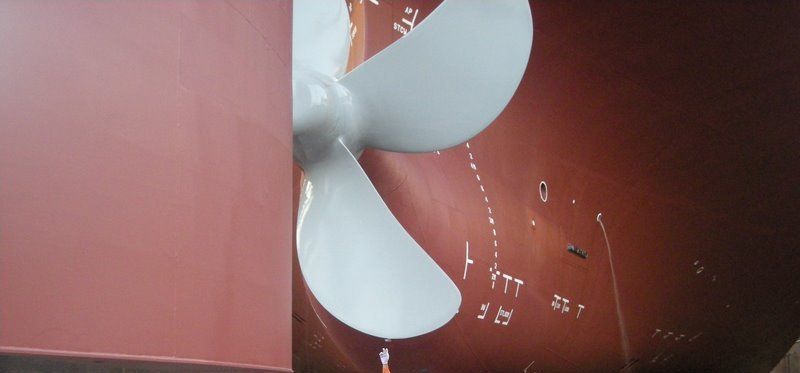
Cavitation of a ship's propeller is phenomena that can greatly reduce a ship propelling efficiency whilst at the same time lead to rapid degradation of the propellor.To learn further about cavitation, we need to get familiar or refresh our knowledge regarding Liquid vapour phases.Solid (ice) Liquid (water) Vapour (steam)The phases of liquid and vapour are influenced by temperature and pressure. Water is normally observed to change its state to the form of vapour when its temperature is raised to above 100 deg C at atmospheric pressure. Water can also vaporise when the … [Read more...]
Basic Propeller Types
Introduction A propeller is a type of fan which generates an adequate thrust to propel a vessel at some design speed with some care taken in ensuring some “reasonable” propulsive efficiency. Considerations are made to match the engine’s power and shaft speed, as well as the size of the vessel and the ship’s operating speed, with an appropriately designed propeller. Generally, propellers are of two types - Fixed Pitch Propeller ( FPP) and Controllable or Variable Pitch Propeller ( CPP). Controllable Pitch Propeller or CPPThese propellers now have a relatively good track record for … [Read more...]