Marpol Regulation 34 Discharges outside special areas Any discharge into the sea of oil or oily mixtures from the cargo area of an oil tanker shall be prohibited except when all the following conditions are satisfied:.1 the tanker is not within a special area; .2 the tanker is more than 50 nautical miles from the nearest land; (This is to make quite certain that the very small amounts of oil permitted to be discharged in compliance with requirements (.4) and (.5)will not reach the shore.) .3 the tanker is proceeding en route; (This eliminates the possible concentration of the permitted … [Read more...]
History of oil transportation at sea
Transportation of oil by water was the indirect result of the first oil well. Mineral oil had been known to exist below the surface of the earth for quite some time. There are indications that the Chinese obtained small quantities from shallow mines several thousand years ago, but the small quantities obtained by them and people inhabiting the Middle East could never have justified the time and energy needed in developing it as a fuel for heating, lighting, and the multitude of other purposes which man has found for oil in the present highly Industrial Age. The first oil well was sunk in … [Read more...]
Recommended Practices for Storage and Transport of Edible Oils and Fats
Introduction The international trade in oils and fats increases every year in volume and diversity. It included some 18 million tonnes of shipped cargo in 1984. The system involved in bringing the products from the harvest field to the end user is complex and inevitably a number of independent management is involved in processing, storage, and transport. It is clearly in the interest of all the parties involved that any deterioration in the products should be minimised. To this end, a number of trade associations have published advice for the benefit of their members. Individual sources … [Read more...]
Deck Water Seal – Inert Gas System on Tankers
Deck Water Seal In an inert gas system onboard Tanker ships, Deck water seal is the principal barrier. A water seal is fitted which permits inert gas to be delivered to the deck main but prevents any backflow of cargo gas even when the inert gas plant is shut down. It is vital that a supply of water is maintained to the seal at all times, particularly when the inert gas plant is shut down. In addition, drains should be led directly overboard and should not pass through the machinery spaces.There are different designs but one of three principal types may be adopted: Wet type This is … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) – Conventional Tanker Basics
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Discharging) Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations.Prior arriving at the discharge port an exchange of information between the ship and the terminal will take place. Once the vessel is tied up at the terminal, a ship-shore checklist will have to be filled out. The general safety checks and precautions will be the same as given for the loadport. Since pumps will be running at the discharge port, special attention will have to be given to monitor the safe running of the pumps. Pumproom ventilation should be running throughout operations. Proper … [Read more...]
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Loading) – Conventional Tanker Basics
Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations. Before a tanker approaches port, there are several factors that must be considered:Testing of cargo/ballast valves, sea valves, pipelines, pumps, inert gas systems, emergency stops. Preparedness of fire-fighting, life-saving and anti-pollution equipment. A pollution drill held before a ship arrives in port will serve the purpose of checking ail equipment. Any response during an emergency will be good since a drill had been executed recently. Preparation of tanks, including readiness of slop tanks. Planning for proper … [Read more...]
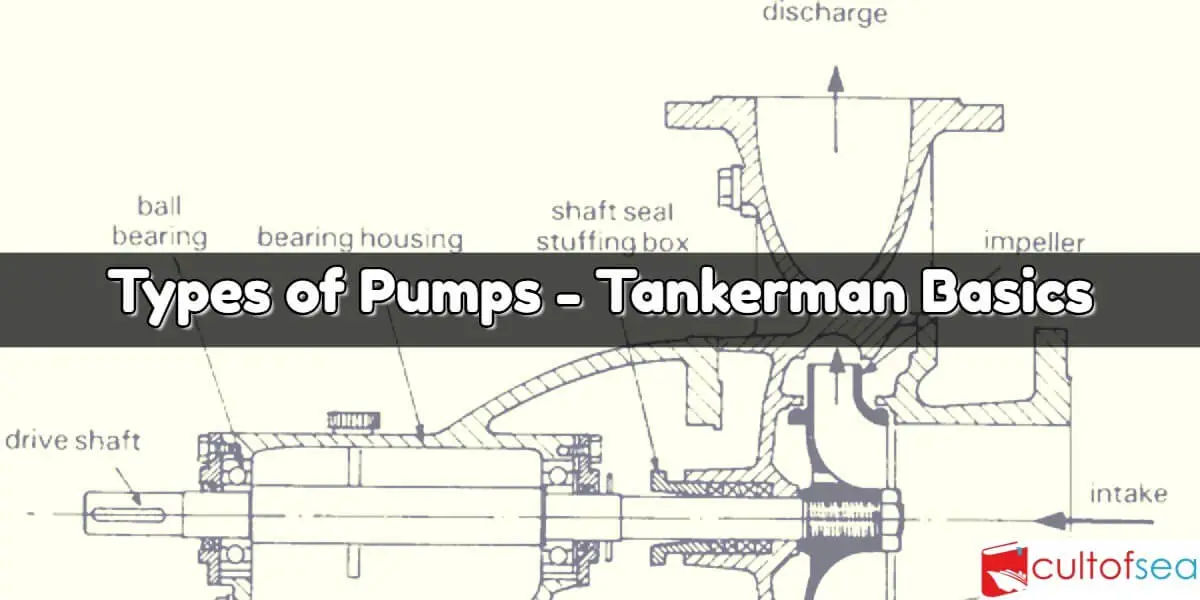
Pump Types / Characteristics – Tanker Basics
There are many types of pumps, each with its own characteristics, advantages and disadvantages. Basically, pumps can be broadly categorised into 3 types :Non-positive-displacement pumps e.g. centrifugal pumps Positive displacement pumps e.g. reciprocating pumps, gear pumps, screw pumps, etc. Special devices like eductors which can also be included in this category.Centrifugal Pumps This type of pump does not have a self-priming capability. Consequently, it operates best only when there is a positive head on the suction side. However, this pump has the distinct capability of … [Read more...]
Piping Arrangement – Conventional Oil Tanker Basics
The arrangement of loading and discharge lines is collectively known as the Ship’s Cargo System. The first oil tankers to carry petroleum products in bulk were equipped with very simple pumping systems. For the most part, they had a single line which ran forward and aft from a midship pump-room, in which were housed two steam reciprocating pumps. One pump served the tanks forward of the pump-room, while the other dealt with the oil from the tanks aft of this pump-room. Some of the more simple types with their engines amidships provided pumps in the engine room to handle the cargo, or … [Read more...]
Control of operational discharge of oil (Machinery Spaces)
Regulation 15 Discharges outside special areas Any discharge into the sea of oil or oily mixtures from ships of 400 gross tonnage and above shall be prohibited except when all the following conditions are satisfied:.1 the ship is proceeding en route;.2 the oily mixture is processed through an oil filtering equipment meeting the requirements of regulation 14 (Oil filtering equipment) of Annex 1;.3 the oil content of the effluent without dilution does not exceed 15 parts per million;.4 the oily mixture does not originate from cargo pump room bilges on oil tankers; … [Read more...]