Voyage Orders The vessel will usually receive voyage orders from the Charterers which will contain the following information:-Ports of loading and discharge along with draft limitations (if any) Volume / Weight to be loaded, grade or grades and Densities involved Special requirements of cargo – e.g. heating Special properties of cargo – e.g. H2SPlanning Cargo Stowage The following factors are to be considered when planning stowage of cargo as applicable:The limiting load line zone of the loaded passage and the port of destination. Draft restrictions during the … [Read more...]
BLU Code – Code Of Practice For The Safe Loading And Unloading Of Bulk Carriers
Purpose The BLU Code has been developed by IMO to minimise losses of bulk carriers. The purpose of the Code is to assist persons responsible for the safe loading or unloading of bulk carriers to carry out their functions and to promote the safety of bulk carriers. The Code primarily covers the safety of ships loading and unloading solid bulk cargoes, excluding grain, and reflects current issues, best practices and legislative requirements. Broader safety and pollution issues such as those covered by the SOLAS, MARPOL and Load Line Conventions are not specifically included in the … [Read more...]
Molasses – Carriage on Tankers
GENERAL Molasses is the thick dark brown syrupy liquid left after sucrose has been removed from the mother liquid in sugar manufacture. There is two type of molasses – cane molasses and beet molasses. Blackstrap molasses is the syrup from which no more sugar can be obtained economically.Synonym of molasses – Treacle.Main composition of molasses at 75 % Dry MatterCane molasses Beet molassesSucrose 30 – 40 % 48 – 52 %Reducing sugars 15 – 20 % 0.2 – 1.2 %Organic non-sugar matter 9 – 12 % 12 – 17 %Sulphated ash 3 – 11 % 3 – 10 % … [Read more...]
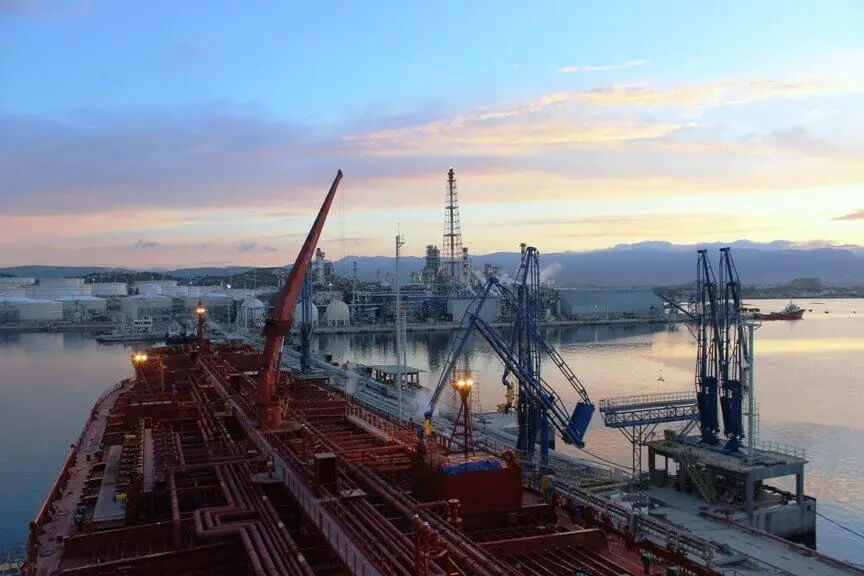
OIL TANKER OPERATIONS (Loading) – Conventional Tanker Basics
Good planning is the hallmark of efficient tanker operations. Before a tanker approaches port, there are several factors that must be considered:Testing of cargo/ballast valves, sea valves, pipelines, pumps, inert gas systems, emergency stops. Preparedness of fire-fighting, life-saving and anti-pollution equipment. A pollution drill held before a ship arrives in port will serve the purpose of checking ail equipment. Any response during an emergency will be good since a drill had been executed recently. Preparation of tanks, including readiness of slop tanks. Planning for proper … [Read more...]
Tanker Terminology used in Shipping
Tanker Terminology Anti-static additiveA substance added to a petroleum product to raise its electrical conductivity to a safe level above 50 picoSiemens/metre (pS/m) to prevent accumulation of static electricity. Auto-ignitionThe ignition of a combustible material without initiation by a spark or flame, when the material has been raised to a temperature at which self-sustaining combustion occurs. BondingThe connecting together of metal parts to ensure electrical continuity. Brush dischargeA brush discharge is a diffuse discharge from a single blunt … [Read more...]