The purpose of a bridge navigational watch alarm system (BNWAS) is to monitor bridge activity and detect operator disability which could lead to marine accidents. The system monitors the awareness of the Officer of the Watch (OOW) and automatically alerts the Master or another qualified OOW if for any reason the OOW becomes incapable of performing the OOW’s duties.This purpose is achieved by a series of indications and alarms to alert first the OOW and, if he is not responding, then to alert the Master or another qualified OOW. Additionally, the BNWAS may provide the OOW with a means of … [Read more...]
AIS (Automatic Identification System)
The Shipborne Automatic Identification System (AIS) is a vessel tracking system capable of communicating navigation information automatically between AIS equipped vessels and coastal authorities. It is a collision avoidance system that gives information all the ships in your area, their speed and courses and how to contact them (name, callsign, MMSI). This information is publically broadcast on VHF radio which can be picked up either by other ships or by shore-based receivers. AIS provides a tool for improved safety and collision avoidance. Since 2004, the International Maritime Organization … [Read more...]
Doppler Log – Principle, Working, Speed and Errors
Doppler log is an instrument, used in ships, to measure ship's relative speed with water (in which it is travelling) by the use of Doppler effects on transmitted/reflected sound waves.PrincipleDoppler log is based on the principle of Doppler shift in frequency measurement i.e. apparent change in frequency received when the distance between source and observer is changing due to the motion of either source or observer or both. In Doppler log an observer is moving with a source of sound towards a reflecting plane, then the received frequency. By measuring the received frequency and … [Read more...]
Echo Sounder – Principle, Working & Errors
One of the dangers faced by a ship is that of running aground. Usually, a vessel determines its position by means of GPS, Radar, Decca, Loran or visual bearings. The depth of water is checked from the echo sounder just as a matter of routine to see that the depth obtained matches with that show on the chart. However when the position is not accurately known while approaching the port, or crossing over a bar, or near the mouth of a river, or in a poorly surveyed area, the under-keel clearance and depth of water needs to be known. The echo sounder comes in handy in such situation.An Echo … [Read more...]
GPS (Global Positioning System)
A network of satellites that continuously transmit coded information, which makes it possible to precisely identify locations on earth by measuring the distance from the satellites. As stated in the definition above, GPS stands for Global Positioning System and refers to a group of U.S. Department of Defense satellites constantly circling the earth. The satellites transmit very low power radio signals allowing anyone with a GPS receiver to determine their location on Earth The 3 Segments of GPS The NAVSTAR system (the acronym for Navigation Satellite Timing and Ranging, the official U.S. … [Read more...]
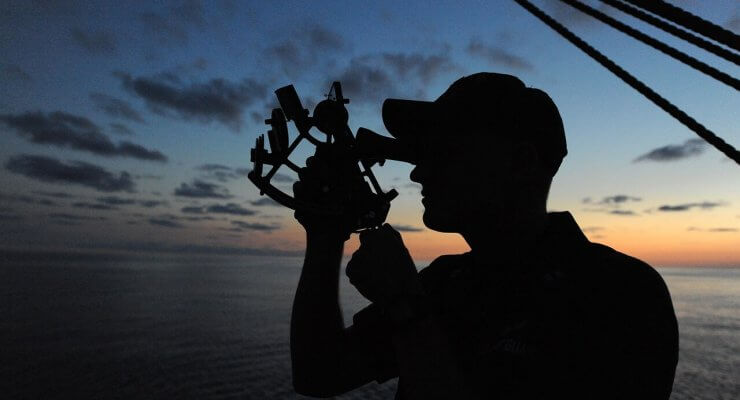
Marine Sextant – Principle and Errors
A sextant is merely an instrument that measures the angle of a heavenly body (star, planet, sun and moon) makes with the visible horizon or the vertical or horizontal angle between two terrestrial objects. It derives its name from the arc at the bottom which is one-sixth of a circle. The principles of a sextant are easy to master but its use requires some skill and practice. Small errors make for large discrepancies in one's position.The trick is to make the celestial body just brush the horizon by a sweeping motion by the wrist - and herein lies somewhat of a knack. The principle of … [Read more...]