The Condition Assessment Scheme (CAS) is intended to complement the requirements of Annex B of the Guidelines on the enhanced programme of inspections during surveys of bulk carriers and oil tankers (hereinafter called Enhanced Survey Programme). The CAS is to verify that the structural condition of single … Continue Reading
Featured Article

International Maritime Organization or IMO: what it is, what it does and how it works ?
International Maritime Organization (IMO) is a specialised agency of the United Nations dealing with maritime affairs , the main concern of which was to evolve international maritime structure to improve safety at sea. Because of the international … Continue Reading
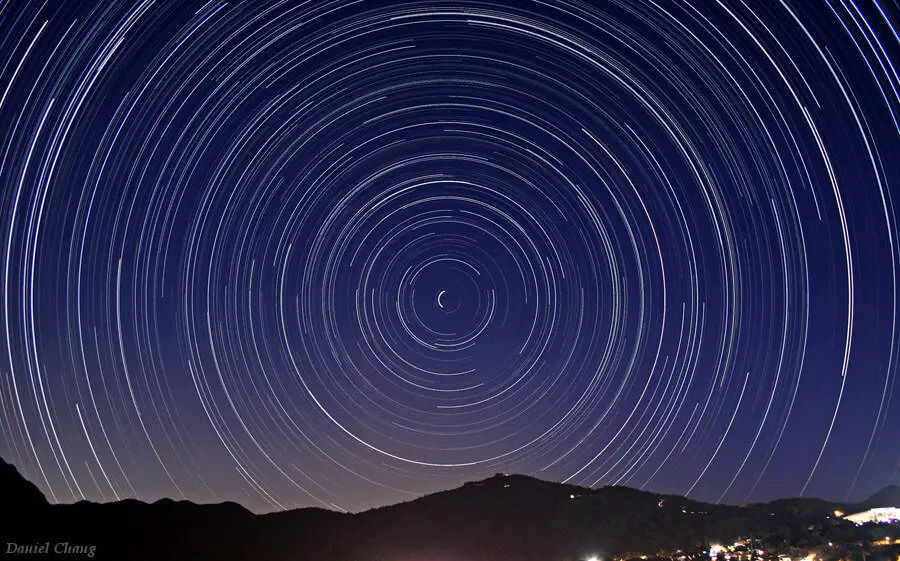

Circumpolar bodies
For a body to be circumpolar, the body should always be above the rational horizon i.e the body should not set. Therefore, a circumpolar body will have upper transit (upper meridian passage) which is above the elevated pole and lower transit (lower … Continue Reading

Fire Wires or Emergency Towing-off Pennants (ETOP’s), MEG 4, ISGOTT Edn 6th Recommendations
Emergency Towing-off Pennants or ETOP's is usually referred to as “ Fire wires,” which provide a method of towing the vessel away from the berth in the event of an emergency. The intent of rigging fire wires or emergency towing pennants is to facilitate the movement of the vessel by tugs without the … Continue Reading

Safety Officer Onboard – Definition, Duties and Powers
Definition of Safety Officer Safety Officer onboard the vessel is an appointed safety adviser who promotes safety onboard by carrying out inspections, identifying hazards and potential hazards to health, safety and the environment with subject to the agreement of the Master. The safety officer should be … Continue Reading

What is General Average & the importance of York-Antwerp Rules ?
General Average There is a General Average act when and only when any extraordinary or expenditure is intentionally and reasonably made or incurred for the common safety, for the purpose of preserving from peril, the property involved in a common maritime adventure. Extraordinary Sacrifice in … Continue Reading

What is a Marine Policy? Basics you need to know!
A contract of Marine Insurance shall not be submitted in evidence unless it is embodied in a Marine Policy accordance with Marine Insurance Act. The policy may be executed and issued either at the time when the contract is concluded or afterwards. Dictionary Meaning of " POLICY " : A set of ideas or a plan … Continue Reading
Documentary Credit System in Shipping – Basics Explained with Flowchart
Documentary Credit System is a payment system used in international trade where the BUYER and SELLER are from different countries. It is developed to include a measure of security to trade transactions by involving a third party, the BANK.The bank provides additional security for both parties i.e. it … Continue Reading

Propeller Cavitation Explained – Cause, Types, Effects & Avoidance
Cavitation of a ship's propeller is phenomena that can greatly reduce a ship propelling efficiency whilst at the same time lead to rapid degradation of the propellor.To learn further about cavitation, we need to get familiar or refresh our knowledge regarding Liquid vapour phases.Solid (ice) … Continue Reading

Technical Aspects of GMDSS Equipments – Propagation, Modulation, Terrestrial Equipment & Antenna
GMDSS Radio Signals Radio signals are transmitted as electromagnetic radiation and occupy the frequency range 3 kHz ~ 300 GHz. The radiofrequency range is divided into a number of bands. In the GMDSS system both terrestrial and satellite methods of communications are interlocked in order to provide an … Continue Reading

Note of Protest vs Letter of Protest – Why, When and Differences between NOP & LOP
Note of Protest Note of Protest or a NOP is a solemn declaration made on oath by a Ship Master that circumstances beyond his control have or may have given rise to loss and/or damage to his ship or its cargo or have caused him to take action which may render owners liable to legal action by another … Continue Reading

Frontal Depressions – Types of Fronts, Weather Associated and Frontolysis
Air Masses It is defined as a quantity of air with dimensions of about 500nm or so, with little or no horizontal variation of any of its properties, especially temperature. Air masses are named after the sources from which they originate. Main air masses on the Earth are Tropical Air Masses and Polar Air … Continue Reading
Clouds – Formation and Ten different Types
General Clouds are a collection of water droplets or ice crystals, or a combination of these two states of water, suspended in the atmosphere.The temperature of the air decreases steadily with increasing altitude, but the amount of water vapor does not necessarily decrease with altitude. Thus, the relative … Continue Reading
