Purpose Ship’s stability calculations not only rely on the ship’s geometry but also on the knowledge of where the ship’s centre of gravity (G) is positioned. Although the distance of G from the keel can be ascertained for various conditions that the ship may be in, it is essential that it is accurately known for one specified ship condition.To this end, the need to carry out an inclining experiment becomes necessary and from this, two facts should become known:the displacement; and the position of G in a known ship’s condition.The inclining test is carried out to find the … [Read more...]
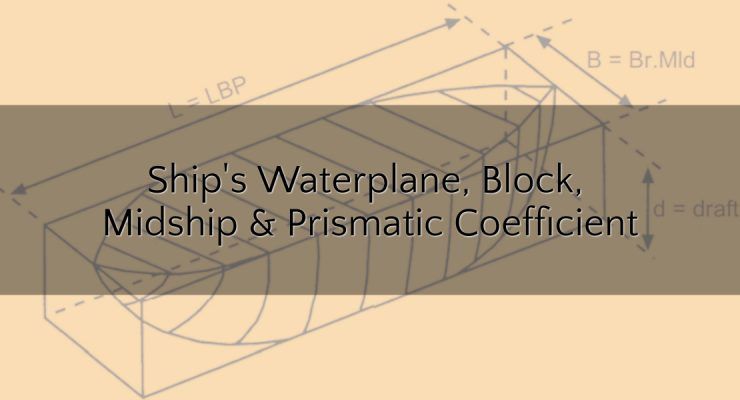
Coefficients of Form – Ship’s Waterplane, Block, Midship and Prismatic Coefficient
The Coefficient of Form shows the relationship between the actual form of the ship and the dimensions of the ship.Waterplane Area Coefficient (Cw) It is the ratio of the actual area of the waterplane to the product of the length and breadth of the ship. As seen below, the area of the ship’s waterplane is shown shaded and a rectangle having the same length and breadth of the ship:Coefficient of fineness (Cw) = Area of waterplane ÷ (Length x Breadth) Example: Q. Find the area of the waterplane of a ship 200 meters long, 30 meters beam, which has a coefficient of fineness of … [Read more...]
Longitudinal Stability for Ships
Any Ship when at rest in calm water, the COB and the COG will be in a vertical line.Pitch Pitch is caused when a wave changes the underwater volume of a ship, making the forces of gravity and buoyancy to get separated by a distance and forming a couple which leads to dip or uplift in the bow or the stern of vessel. The up and down movement of the ship's ends, due to longitudinal shift of COB resulting from wave action, is called pitch.If a wave cause an increase in the underwater volume aft, and a decrease fwd, the COB will shift aft. The forces of gravity and buoyancy will now get … [Read more...]
Ship Stability Definitions related to Hydrostatic Particulars
Density of a substance is its mass per unit volume, normally expressed as tonnes per cubic metre in ship calculations.Relative Density of a substance is the ratio between the density of that substance and the density of fresh water.Displacement of the ship is the weight of the ship and its contents or the weight of water displaced by the ship in that condition.Displacement = Underwater volume of the ship x the density of the water in which she is floating.It should be noted that the volume of displacement is the underwater volume of the ship. When a ship proceeds from water of … [Read more...]