A barometer is an instrument for measuring the pressure of the air, due to the weight of the column of air above it. As the earth’s atmosphere gets thinner with increasing height, it follows that as we ascend from sea level and low-lying parts of the earth’s surface, the weight of the air will decrease. That is, the pressure will fall.

An ordinary clock face type barometer placed in your car will give an estimate of the changes in altitude as you drive through the country. If we use rough figures, we can say that the reading decreases by three hectopascals for each twenty-five metres of ascent. For example, if the barometer reads 1020 hectopascal at the sea coast and you drive along a mountain road 325 metres high, the pointer should move down the scale to about 980 hectopascals.
A barometer’s main use, however, is not to measure altitude, but to measure the actual changes in the pressure of air at a particular place. High and low-pressure systems in the atmosphere move around the earth’s surface and the movements shown on the face of a barometer attached to the wall of your home indicate the changes of pressure as they occur directly above you. These changes, when they are considered together with wind, temperature, moisture and cloud indications, can be a great help in forecasting approaching weather.
Who invented it?
About 1645, an Italian mathematician named Torricelli discovered the principle of the barometer by using a long glass tube closed at one end, which he put upside down in an open container holding liquid. He found that the pressure of the air bearing down on the liquid in the container forced it up the tube, and the measurement of the various lengths of the column of liquid was, therefore, a means of expressing the changes in air pressure. In order to have a tube of manageable length, the heaviest of all liquids, mercury, was later used.
Today we have finely constructed mercurial barometers capable of giving very accurate readings. They are costly and they need special care in handling. For general use, an easier though less precise means of measurement has been devised – the ANEROID BAROMETER (aneroid = without fluid).
How does it work?
The aneroid barometer is operated by a metal cell containing only a very small amount of air, or a series of such cells joined together. The increased air pressure causes the sides of the cell or cells to come closer together. One side is fixed to the base of the instrument while the other is connected by means of a system of levers and pulleys to a rotating pointer that moves over a scale on the face of the instrument. This pointer is usually black.

The aneroid barometer (below) consists of a closed sealed capsule with flexible sides. Any change in pressure alters the thickness of the capsule. When the atmospheric pressure increases, the cell gets compressed and the inward movement of the cell wall is transmitted to the pointer mechanically and it then registers a higher reading on the scale.
Levers magnify these changes, causing a pointer to move on a dial, or numbers to change on a digital read-out device.
Use of the barometer in forecasting
To repeat what was said at the beginning, a barometer is an instrument which measures air pressure. It does NOT foretell weather, so you would be well advised to put little faith in the words STORMY, RAIN, CHANGE, FAIR and DRY which appear on the face of many popular makes of barometer. The pressure may well never fall to the values shown for Stormy or Rain for most places within Australia.
Many of you will know from the weather charts that highs and lows move in general from west to east, especially in the more southern latitudes. Bad weather is often associated with the lows, though moist onshore winds can cause rain in coastal areas even if the pressure is high. In other words, the actual reading of the barometer does not give unmistakable information concerning the weather to come.
Your barometer will show whether the pressure is rising or falling, that is, whether a high or low-pressure system is approaching, or perhaps developing in intensity.
But here, a word of caution! Owing to a daily atmospheric tide effect, the pressure will normally fall by about three hectopascals between 9 am and 3 pm and will rise by a nearly similar amount between 3 pm and 9 am, even if weather systems are stationary. A smaller rise and fall occurs during the night and early morning. These daily (diurnal) changes must be allowed for before you can really say whether pressures are rising or falling due to weather systems. The best way to avoid this difficulty is to observe changes over 24-hour periods, using your movable set pointer. In other words, check your barometer at the same time each day.
When there is a fairly large fall, say more than seven hectopascals in 24 hours, you can assume that a high is moving away or that a depression is approaching or both.
Reading your barometer
To read your barometer, first tap the glass lightly, but firmly, to ensure that the linkage mechanism is not sticking. Your barometer will most likely be marked in tens of hectopascals (990, 1000, 1010 etc.) with further graduations given for each hectopascal, which enable it to be read reasonably easily to the nearest half hectopascal.
Perhaps your barometer is graduated in millimetres (if it is of European manufacture) or only in inches (if it is not of recent manufacture). Here is a conversion table which will help you.
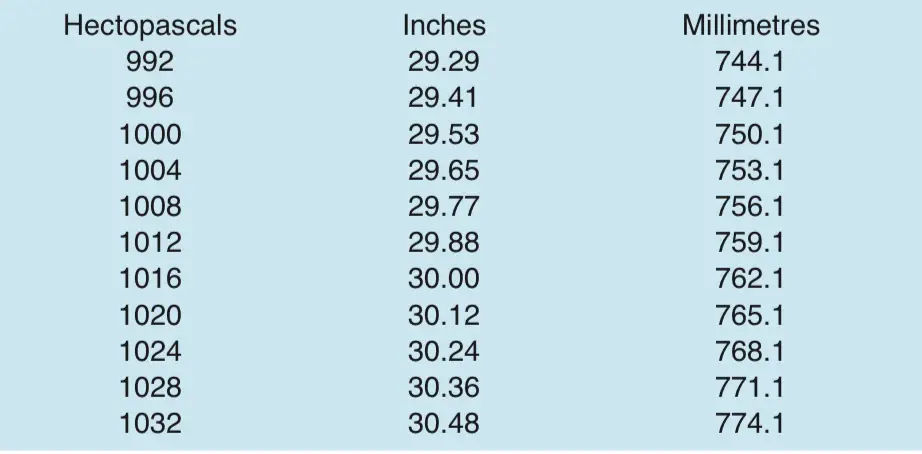
The other hand that is found on most instruments is the ‘set pointer’ (usually brass). This can be turned by means of the knob at the centre of the glass so that it covers the reading pointer. In this way, you can tell, next time you check your barometer, whether the pressure is now lower or higher and by how much.
Adjusting your barometer
So that we can compare readings made at sea level with those made at more elevated places, where the pressure of the air is much lower, we must establish a uniform standard. Therefore all pressures must be reduced to mean sea level, or in other words, to the pressure, each barometer would record if it were at sea level directly below the place where it is situated. Your barometer, too, must be set to show sea level pressure if it is to give readings that can be compared with official barometric reports and used as a weather indicator.
Official barometric readings, corrected to sea level, are broadcast by some radio stations. After noting the times of the barometric readings which are broadcast or published, you can note the reading of your barometer at one of these times and compare it with the official reading at the same time.
Also, you can forward your request to nearest coast station or directly to Regional Office of the Bureau of Meteorology in current State or Territory. An officer will compare your reading with the isobaric chart and tell you what adjustment (if any) is needed.
If your reading is different from the official reading an adjustment can be made by turning the screw at the back of the instrument, tapping the barometer lightly while using the screwdriver.
Leave a Reply