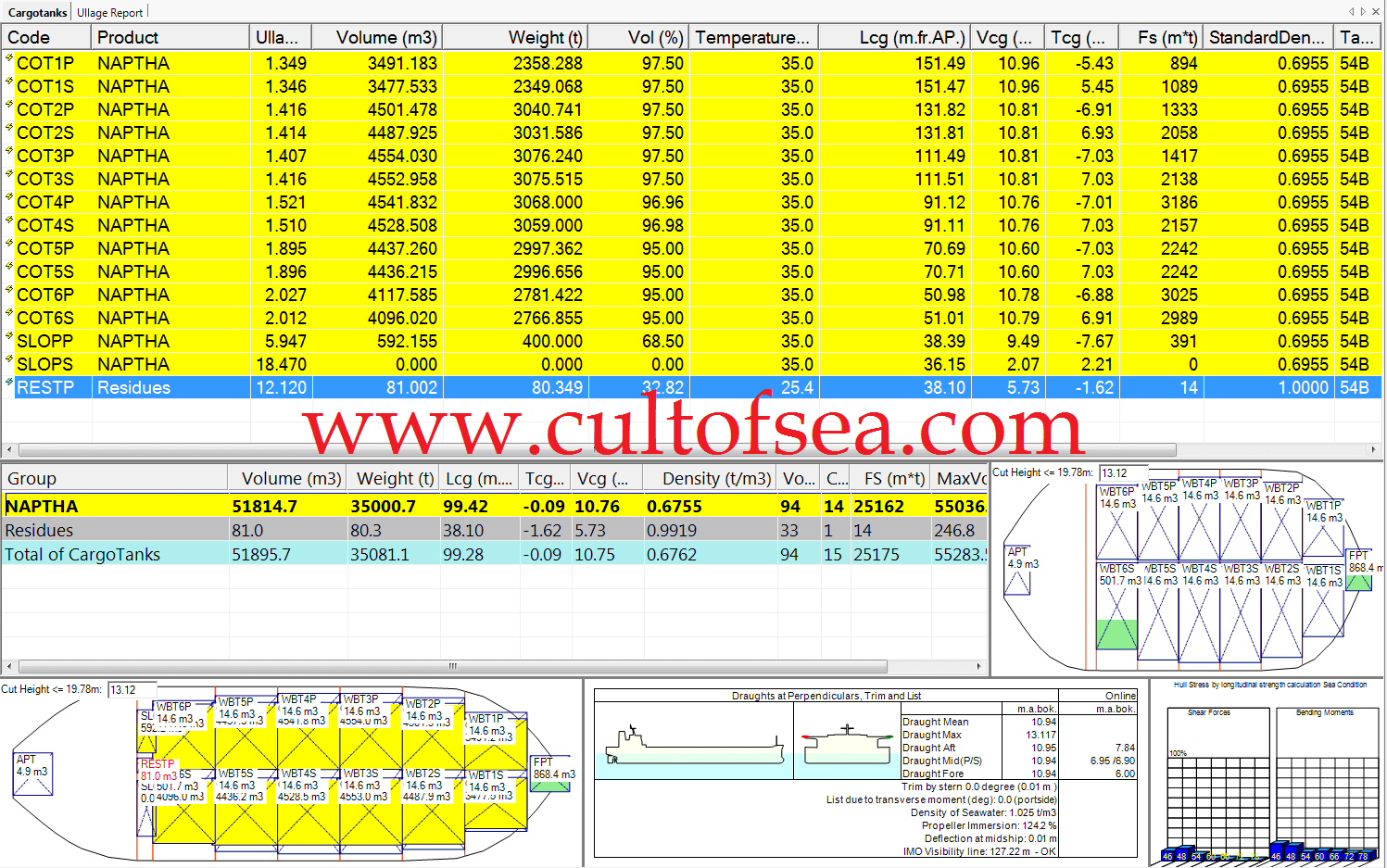
Density of a substance is its mass per unit volume, normally expressed as tonnes per cubic metre in ship calculations.Relative Density of a substance is the ratio between the density of that substance and the density of fresh water.Displacement of the ship is the weight of the ship and its contents or the weight of water displaced by the ship in that condition.Displacement = Underwater volume of the ship x the density of the water in which she is floating.It should be noted that the volume of displacement is the underwater volume of the ship. When a ship proceeds from water of … [Read more...]
Archives for January 2016
Static Electricity / Electrostatic Hazards
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it is able to move away by means of an electric current or electrical discharge. Static electricity is electricity that does not flow in a current. Static electricity generated by rubbing two nonmagnetic objects together. The friction between the two objects generates attraction because the substance with an excess of electrons transfers them to the positively-charged substance. Usually, substances that don't conduct current electricity (insulators) are good at holding a … [Read more...]
What is Load on Top (LOT)?
Not all oil pollution is caused by tankers. However, the huge volume of crude oil transported by sea has created a major problem in disposing of dirty ballast and tank washings without harming the marine environment or damaging coastal amenities. Most crude oils contain wax and other materials in solution, together with sediments, which may settle out during the voyage and form a residue with any cargo remaining after discharge (of the order of 0.2 to 0.5 per cent of the cargo carried). If discharged into the sea in heavy concentrations in the course of tank washing the residue will stay on … [Read more...]
Principles of Ship Handling
Ship Handling and Maneuvering is defined as the art of proper control of a ship while underway, especially in harbours, around docks and piers. It is one of the skills that any ship handler finds very satisfying when well accomplished. The most basic thing to be understood in ship handling is to know and anticipate how a ship behaves under all circumstances and what orders should be given in order to make the ship behave and move exactly the way you want her to. The difference between the ships' heading and the actual direction of movement of the ship should also be constantly attended to as … [Read more...]
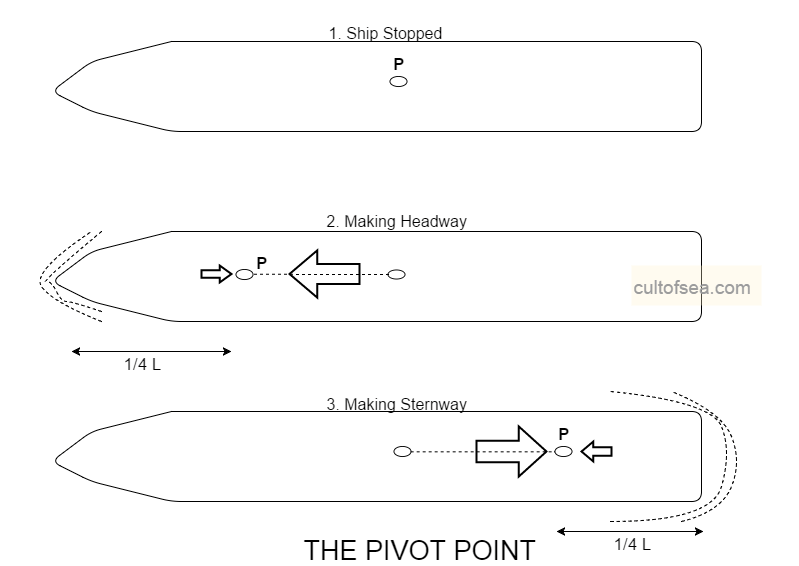
The Pivot Point
A Pivot Point is a central point on a vessel which remains fixed as the bow and stern swing around it. Fixed is not really correct, because it moves forward or aft as the vessel moves through the water as stated below: 1. Ship stopped Unless stated otherwise. Each example assumes a ship on an even keel in calm conditions and still water. In this situation, no forces are involved and the ship has a pivot point coinciding with its centre of gravity approximately amidships.2. Making Headway Two forces now come into play. Firstly the forward momentum of the ship and secondly, longitudinal … [Read more...]
Circumpolar bodies
For a body to be circumpolar, the body should always be above the rational horizon i.e the body should not set. Therefore, a circumpolar body will have upper transit (upper meridian passage) which is above the elevated pole and lower transit (lower meridian passage) which is below the elevated pole.Condition required for a body to be circumpolar:Lat + Dec > 90° (For the body not to set)Latitude and declination should be the same name.1. North Latitude - Lat < Dec2. North Latitude - Lat > Dec3. South Latitude - Lat < Dec4. … [Read more...]
Twilight
Twilight is the light received from the sun, when the sun is below the horizon, i.e. before the sunrise and after the sunset.Twilight completely ceases in the evening, when the sun is 18° vertically below the horizon. After that, there is total darkness.In the mornings, twilight commences when the sun is 18° vertically below the horizon and ceases at sunrise.The entire period of twilight has 3 stages, Civil, Nautical and Astronomical.Astronomical commences when the sun is 18° below the horizon.Nautical - 12° below the horizon.Civil - 6° below the … [Read more...]
Rising and Setting of Celestial Bodies
As the Earth rotates on its axis from west to east, all heavenly bodies appear to rise in the east, move westwards, gaining in altitude until it is on the observer's meridian (culminate or transit the meridian). After culmination, it continues to move westwards decreasing in altitude till it sets over the western horizon.For a stationary observer, the interval between rising and culmination of a body will be equal to the interval between its culmination and setting, provided its declination remains unchanged.Also under the same circumstances, its amplitude at rising will be equal to … [Read more...]
IALA Buoyage System
The International Association of Marine Aids to Navigation and Lighthouse Authorities (IALA) is a non-profit organization founded in 1957 to collect and provide nautical expertise and advice.• Lateral marks indicate the edges of a channel.• Cardinal marks indicate the direction of safe water at a dangerous spot.• Safe water marks indicate the deep water and open end of a channel.• Special marks indicate administrative areas, such as speed restrictions or water skiing areas.• Isolated danger marks indicate a hazard to shipping. Lateral MarksRegion A Region A comprises … [Read more...]