Operating Principle Biological Sewage Treatment System DVZ-SKA- BIOMASTERThe Biological Sewage Treatment system consists of three watertight compartments and other equipment:1. Pre-treatment Tank2. Treatment Tank3. Disinfecting Tank4. Other Equipment (pumps, blowers, dosing pumps, level sensor)PRE-TREATMENT TANKThe "black water" is fed through the pipeline using gravity or a vacuum and flows through the sewage inlet into the pre-treatment tank, where intensive sedimentation and pre-treatment takes place using oxygen, a continuous supply of which is provided by a … [Read more...]
Archives for December 2015
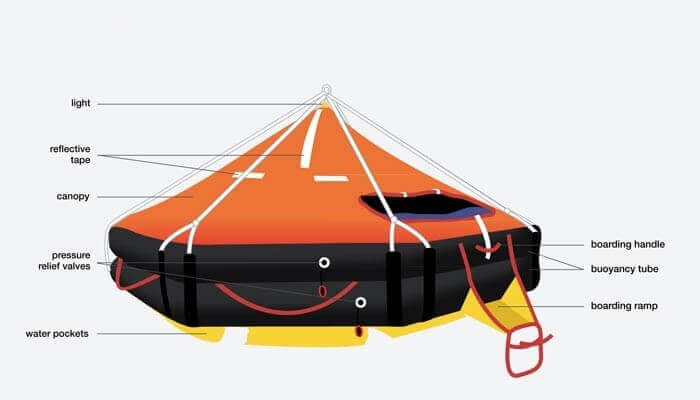
Liferaft – General Requirements
General RequirementsEvery liferaft shall be so constructed as to be capable of withstanding exposure for 30 days afloat in all sea conditions. The liferaft shall be so constructed that when it is dropped into the water from a height of 18 m, the life raft and its equipment will operate satisfactorily. If the life raft is to be stowed at a height of more than 18 m above the waterline in the lightest seagoing condition, it shall be of a type which has been satisfactorily drop-tested from at least that height. The floating life raft shall be capable of withstanding repeated jumps onto … [Read more...]
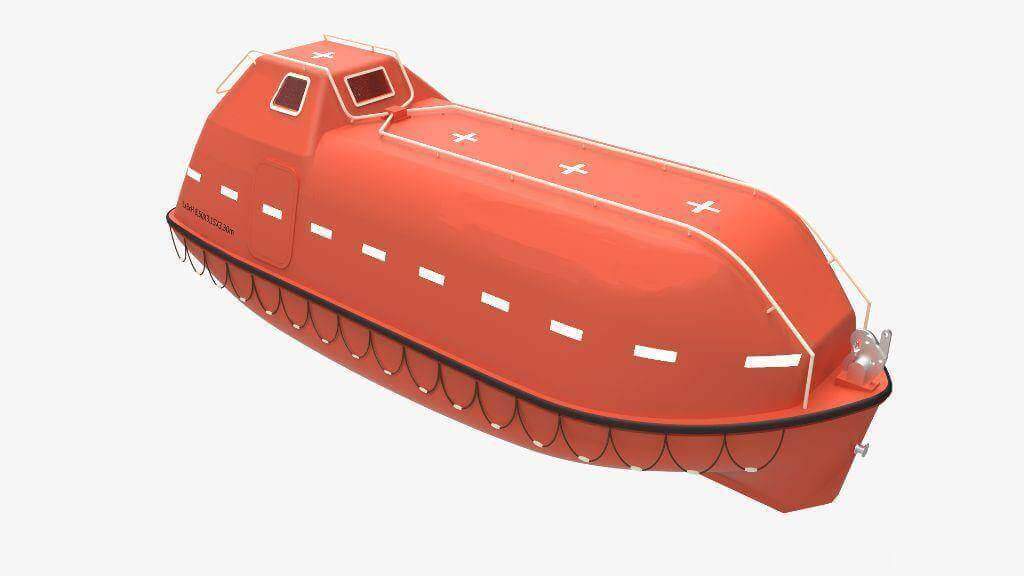
Lifeboat – General Requirements
Requirements All lifeboats shall be properly constructed and shall be of such form and proportions that they have ample stability in a seaway and sufficient freeboard when loaded with their full complement of persons and equipment. All lifeboats shall have rigid hulls and shall be capable of maintaining positive stability when in an upright position in calm water and loaded with their full complement of persons and equipment and holed in any one location below the waterline, assuming no loss of buoyancy material and no other damage.1. Each lifeboat shall be fitted with a certificate of … [Read more...]
What is Transverse Thrust?
Transverse Thrust The force with which the water acts upon the propeller blades is not just in the longitudinal direction but also has an athwartships component. This is known as transverse thrust. Going Ahead If we look at a ship with one right-handed propeller (i.e. the propeller rotating n a clockwise direction when going ahead and as viewed from astern) and the rudder on the centre line the following situation is the norm: In the initial stages of the ship getting underway, the vessel's speed is low but the engine (and, therefore, the propeller) is at high Rpm ahead. During this … [Read more...]
Shallow Water Effect on Ship
Shallow water effects on a ship w.r.t "Draft & Maneuverability." • As the hull moves through shallow water, the area which it displaces is not so easily replaced by surrounding water, therefore, leading to a state of partial vacuum as the propeller and rudder are still working. The vessel take-ups longer to answer her helm, and response to engine movements becomes sluggish.• In these circumstances, vibration will be set up, and it will be extremely difficult to correct a yaw or sheer with any degree of rapidity.• At normal speed it is found that steering becomes erratic when the … [Read more...]
How do you make out if the Anchor is dragging?
It can take some time to realise the Anchor is dragging, despite the ship drifting. A vigilant bridge watch is, therefore, essential.By watching the bearing of two fixed lights or objects in line. Beam bearings are the best. If they change, the ship is dragging. By dropping the deep sea lead on to the bottom, and noting if it trails ahead of the ship. By observing the anchor cable if she comes to long stay then short stay and then long stay repeatedly means she is dragging anchor. The ship’s side against the wind hasn’t changed. Checking to see there is no slacking of chains … [Read more...]
Solar system and Kepler’s law of Planetary Motion
Solar systemConsists of the Sun, the planets, the planetary satellites, asteroids, comets and meteors. Sun has a dia (865,000 miles) of more than 700 times larger than all the other bodies taken together. It is the only body of the solar system which radiates light. It rotates about its own axis, completing one rotation in about 25 days. There are eight non-luminous planets which we see only because they reflect light and they exhibit phases like the moon. In order of distance from the sun, they are Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. Between … [Read more...]
Revised High Risk Area – BMP4 effective 1 December 2015
Section 2 of BMP 4 effective 1 December 2015 : Somali Pirate Activity - The High-Risk Area The High-Risk Area (HRA) is an area within the UKMTO designated Voluntary Reporting Area (VRA) where it is considered there is a higher risk of piracy and within which self protective measures are most likely to be required.The High-Risk Area is now defined as being bounded by:In the Red Sea: Latitude 15 N In the Gulf of Oman: Latitude 22 N Eastern limit: Longitude 065 E Southern limit: Latitude 05 SIt should be noted military threat assessments provided by SHADE indicate that the … [Read more...]
Heavy Lift Cargo – Precautions and Stability Changes Onboard Merchant Ships
Precautions for Heavy Lift OnboardCarry out a “Risk Assessment” prior to commencing the operation to ensure that all possible areas of hazard are taken account of and that all risks are at an acceptable, tolerable risk level. Ensure that the stability of the vessel is adequate to compensate for the anticipated angle of heel that be experienced when the load at the maximum angle of outreach. All free surface elements should be reduced or eliminated, if possible, to ensure a positive value of GM throughout the operation. Any additional rigging, such as “preventer backstays” should … [Read more...]
Pyrophoric Iron Fires
At one time or another, most refineries experience spontaneous ignition of iron sulphide either on the ground or inside equipment. When this occurs inside equipment like columns, vessels, and tanks and exchangers containing residual hydrocarbons and air, the results can be devastating. Most commonly, pyrophoric iron fires occur during shutdowns when equipment and piping are opened for inspection or maintenance. Instances of fires in crude columns during turnarounds, explosions in sulphur, crude or asphalt storage tanks, overpressures in vessels, etc., due to pyrophoric iron ignition are not … [Read more...]